What Is Blockchain?
The Next Step After the Internet
You use the Internet every day. It's a revolutionary technology for sharing information—text, images, and videos can be sent across the globe almost instantly. But the internet wasn't built to transfer value (like money or property) securely without a middleman. That's why we still rely on banks.
Blockchain is the next great technological leap. It's a new kind of digital foundation designed specifically to transfer value securely, without needing to trust a central authority.
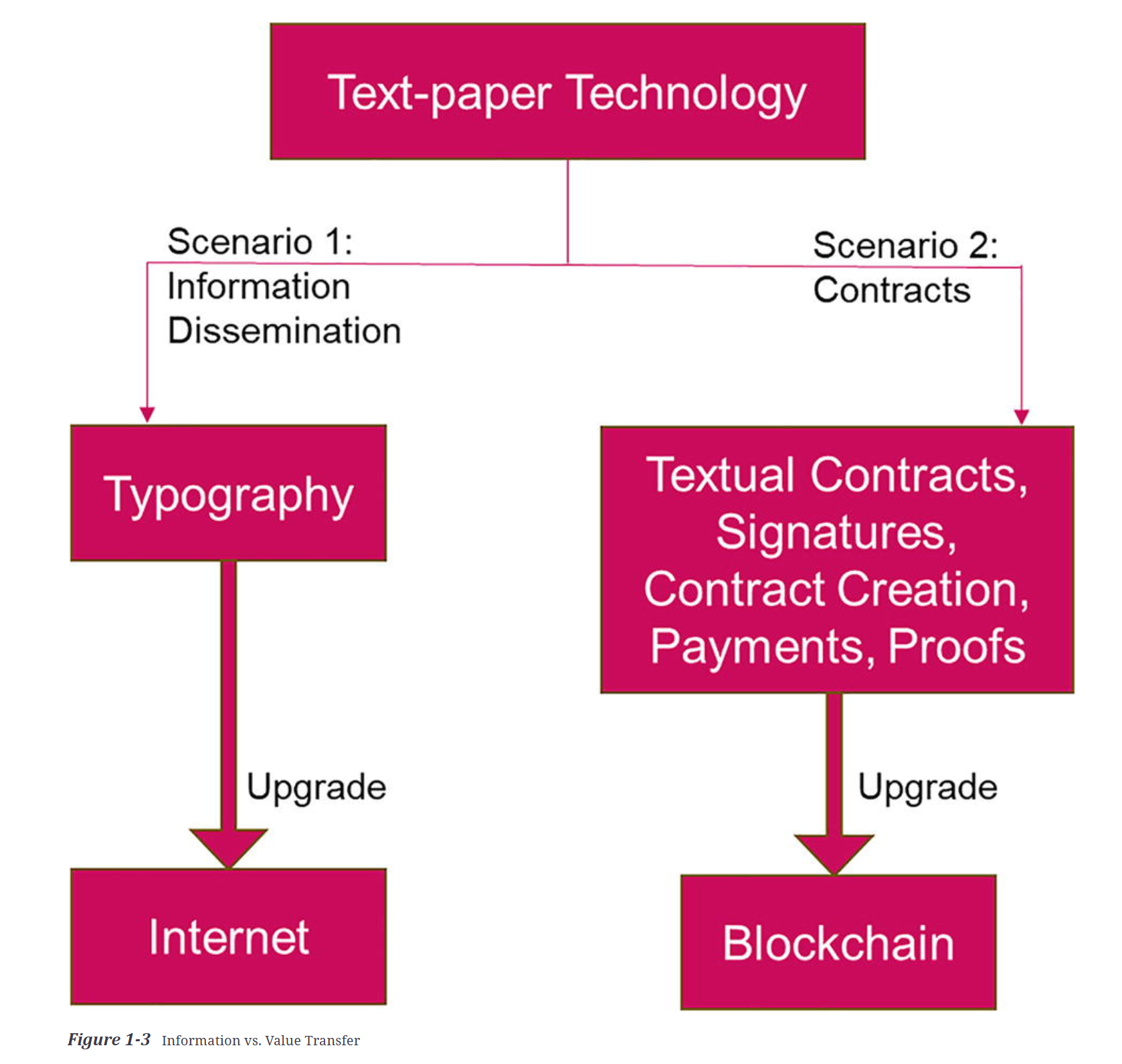
Figure 1-3 outlines the evolution of technology from text-paper to digital formats. At the top, the ‘Text-paper technology’ serves as the starting point. And then one path lead to to ‘Typography’, eventually evolving into the ‘Internet'. The other path leads to ‘Textual Contracts, Signatures, Contract Creation, Payments, Proofs’, which then lead to ‘Blockchain’, representing the digitisation of contractual and transactional processes.(Gong, 2024)
The key takeaway is that while the Internet evolved as the digital successor for text and information, blockchain serves a similar role for transactions and value.
The Core Idea: A Shared, Unchangeable Digital Record!
At its heart, a blockchain is a digital record book with three magical properties, based on the technology first introduced with Bitcoin in 2008:
Decentralized
Instead of one company owning the record book, every participant holds an identical copy. There is no central point of control or failure. This distribution is what builds trust.
Immutable
New transactions are bundled into 'blocks' and are cryptographically chained to the previous block. Once a block is added, it is nearly impossible to alter, creating a permanent history.
Transparent
While users can remain anonymous, the list of transactions on a public blockchain is open for anyone to see and verify. This openness ensures no one can cheat the system.
Blockchain 1.0: Solving Two Classic Problems
The first version of blockchain, which powers Bitcoin, was a genius solution to two famous challenges in computer science:
- The Double-Spending Problem: Answers the question, "How do you make sure a digital dollar is only spent once?" by using a public record everyone agrees on.
- The Byzantine Generals' Problem: A metaphor for, "How can a decentralized group who don't trust each other agree on a single truth?" Blockchain solves this with a consensus mechanism.
Now that you understand the basic concept, you're ready to explore where this technology is heading.
The Next Frontier: Web3 and the Metaverse
Blockchain is a core component of what many call the "Next Generation Internet" or Web3. The goal is to build a more decentralized, secure, and user-controlled version of the internet. This future internet is envisioned as a "metaverse"—a virtual world not controlled by a single company, where users can interact, own digital assets, and conduct business securely **(Avasthi et al., 2024)**. While still in development, this vision highlights that blockchain's importance will only grow as our lives become more digital.
Next: Blockchain 2.0 & Smart Contracts